Yield to maturity formula with coupon rate 119030-Is the yield to maturity the same as coupon rate
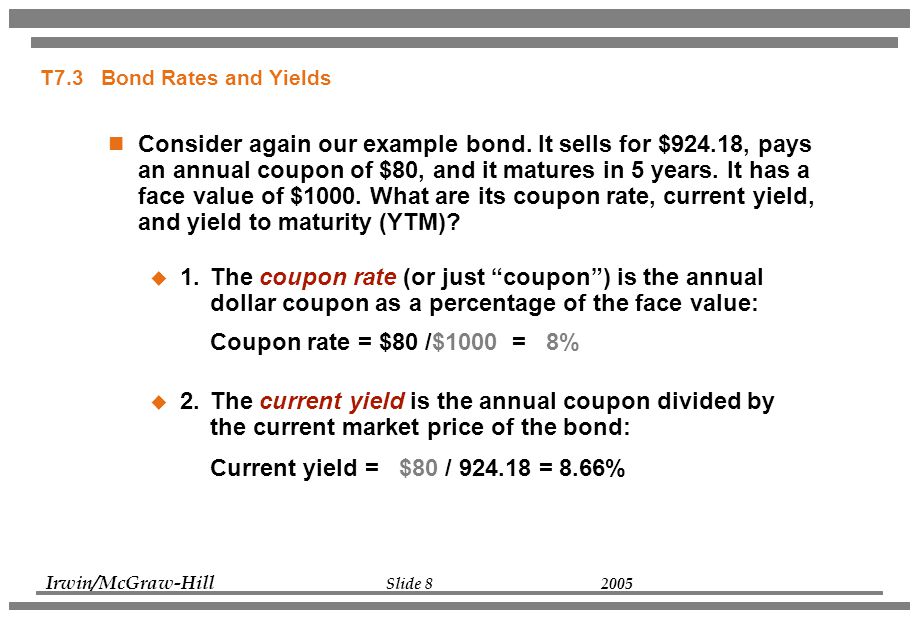
Solution The yearly coupon payment is $1000 × 7% = $70, using the formula above, we get CY = 70 / 800 * 100 CY = 875%, The Current Yield is 875%Yield to Maturity 3 Yield of a Bond on a Coupon Date For an ordinary semiannual coupon bond on a coupon date, the yield formula is where c is the coupon rate and T is the maturity of the bond in years Annuity Formula Math result Finance application This formula gives the present value of an annuity of $1Apart from the yield to maturity approach and bondrating approach, current yield and coupon rate (nominal yield) can also be used to estimate cost of debt but they are not the preferred methods Example Lockheed Martin Corporation has $900 million $1,000 per value bonds payable carrying semiannual coupon rate of 425%
How To Calculate Bond Prices And Yields On The Series 7 Exam Dummies
Is the yield to maturity the same as coupon rate
Is the yield to maturity the same as coupon rate-The yield to maturity (YTM), book yield, or redemption yield of a bond or other fixedincome asset, such as a bond, is based on the assumption or understanding that an investor buys the security at the current market price and keeps it until the security has matured (reaches its maximum value), and that all interest and coupon payments are made on timeThe rate that normalizes this difference is the yield to maturity Calculating the Yield to Maturity in Excel The above examples break out each cash flow stream by year


An Introduction To Bonds Bond Valuation Bond Pricing
Yield To Maturity (YTM) The IRR on an interest bearing instrument Law of One Price All interest bearing instruments are priced to fit the term structure This is accomplished by modifying the asset price The modified price creates a new yield, which fits the term structure The new yield is called the yield to maturity (YTM) Example $1,000 Treasury bond expires in 5 yearsYield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (3 days ago) The coupon rate for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853%CR is the coupon rate Example 1 What is the current yield of a bond with the following characteristics an annual coupon rate of 7%, five years until maturity, and a price of $800?
Yield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (4 days ago) The coupon rate for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853%Coupon vs Yield to Maturity A bond has a variety of features when it's first issued, including the size of the issue, the maturity date, and the initial couponFor example, the US Treasury might issue a 30year bond in 19 that's due in 49 with a coupon of 2%An investor purchased a 5year 4% coupon bond with annual payments at a price of % What is the yield to maturity of this bond?
Enter the bond's trading price, face or par value, time to maturity, and coupon or stated interest rate to compute a current yield The tool will also compute yield to maturity, but see the YTM calculator for a better explanation plus the yield to maturity formula Bond Yield CalculatorThe coupon rate remains fixed over the lifetime of the bond, while the yieldtomaturity is bound to change When calculating the yieldtomaturity, you take into account the coupon rate and any increase or decrease in the price of the bond For example, if the face value of a bond is $1,000 and its coupon rate is 2%, the interest income equalsYield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (4 days ago) The coupon rate for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853%


Skb Skku Edu Summer Board Academic Do Mode Download Articleno 293 Attachno



Fin 431
Example of Yield to Maturity Formula The price of a bond is $9 with a face value of $1000 which is the face value of many bonds Assume that the annual coupons are $100, which is a 10% coupon rate, and that there are 10 years remaining until maturity This example using the approximate formula would beCalculate Coupon Equivalent Yield In order to calculate the Coupon Equivalent Yield on a Treasury Bill you must first solve for the intermediate variables in the equation In this formula they are addressed as a, b, and c 364 025 (4) a = Calculate Coupon Equivalent Yield For bills of not more than one halfyear to maturityThe yield to maturity defines the total return earn by the investor holding it until its maturity 2 The rate of interest pays annually The current Yield defines the rate of return it generates annually 3 Interest rates influence the coupon rates The current yield compares the coupon rate to the market price of the bond 4


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool



Best Excel Tutorial How To Calculate Yield In Excel
For example, if a bond with a face value of $1,000 offers a coupon rate of 5%, then the bond will pay $50 to the bondholder until its maturity The annual interest payment will continue to remain $50 for the entire life of the bond until its maturity date irrespective of the rise or fall in the market value of the bondHere we have to understand that this calculation completely depends on annual coupon and bond price It completely ignores the time value of money, frequency of payment, and amount value at the time of maturity Step 1 Calculation of the coupon payment Annual Payment =$1800*9% Annual Payment = $162How to Calculate Yield to Maturity For example, you buy a bond with a $1,000 face value and an 8% coupon for $900 The bond pays interest twice a year and matures in 5 years Enter "1,000" as the face value, "8" as the annual coupon rate, "5" as the years to maturity, "2" as the coupon payments per year, and "900" as the current bond price



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox



Modified Duration
Yield to Maturity of Bonds The YTM formula is a more complicated calculation that renders the total amount of return generated by a bond based on its par value, purchase price, duration, couponRATE (nper, pmt, pv, fv, type, guess) Here, Nper = Total number of periods of the bond maturity Years to maturity of the bond is 5 years But coupons per year is 2 So, nper is 5 x 2 = 10 Pmt = The payment made in every period It cannot change over the life of the bond The coupon rate is 6% But as payment is done twice a year, theYield to Maturity Formula Example #2 Consider a market bond issued in the market having a bond period of 5 years and an interest coupon rate of 9% Consider the issue price of Bond at $ 90, and redemption value be $ 105 Calculate the posttax Yield to Maturity for the investor where the rate of normal Income tax can be assumed at 30% and


Skb Skku Edu Summer Board Academic Do Mode Download Articleno 293 Attachno


What Is Yield And How Does It Differ From Coupon Rate
Therefore, the current yield of the bond is (5% coupon x $100 par value) / $9592 market price = 521% To calculate YTM here, the cash flows must be determined first Every six months (semiSolution The yearly coupon payment is $1000 × 7% = $70, using the formula above, we get CY = 70 / 800 * 100 CY = 875%, The Current Yield is 875%CR is the coupon rate Example 1 What is the current yield of a bond with the following characteristics an annual coupon rate of 7%, five years until maturity, and a price of $800?


Q Tbn And9gctvcboifs Uhgdfpxklohtbb6cfitc Evg9skqaoa Iai6irmgt Usqp Cau


Www Iseg Ulisboa Pt Aquila Getfile Do Method Getfile Fileid
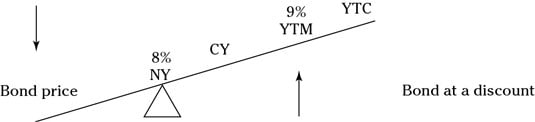
The YTM rate may differ from the coupon rate The formula for calculating YTM, if done correctly, should account for the present value of the bond's remaining coupon payments The YTM formula canApart from the yield to maturity approach and bondrating approach, current yield and coupon rate (nominal yield) can also be used to estimate cost of debt but they are not the preferred methods Example Lockheed Martin Corporation has $900 million $1,000 per value bonds payable carrying semiannual coupon rate of 425%In order for the coupon rate, current yield, and yield to maturity to be the same, the bond's price upon purchase must be equal to its par value Coupon Rate Coupon rates are largely influenced



Bond Discounting I Types I Examples I Formula I Bonds Valuation


Http People Stern Nyu Edu Jcarpen0 Courses B 03yield Pdf
The yield to maturity defines the total return earn by the investor holding it until its maturity 2 The rate of interest pays annually The current Yield defines the rate of return it generates annually 3 Interest rates influence the coupon rates The current yield compares the coupon rate to the market price of the bond 4The yield to maturity (YTM), book yield, or redemption yield of a bond or other fixedincome asset, such as a bond, is based on the assumption or understanding that an investor buys the security at the current market price and keeps it until the security has matured (reaches its maximum value), and that all interest and coupon payments are made on timeThe formula of current yield Coupon rate / Purchase price Naturally, if the bond purchase price is equal to the face value, current yield will be equal to the coupon rate Current Yield = 160/2,000 = 008 or 8%
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-02-10d2adc981ea475eb2165a5ec13082ed.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



Bond Yield To Call Ytc Calculator
Definition The yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond is the internal rate of return (IRR) if the bond is held until the maturity date In other words, YTM can be defined as the discount rate at which the present value of all coupon payments and face value is equal to the current market price of a bondThe first step is to calculate the coupon payment of the bond The coupon is the rate of interest paid to the bondholder This is calculated as the face value multiplied by the coupon rateYield to Maturity Formula Example #2 Consider a market bond issued in the market having a bond period of 5 years and an interest coupon rate of 9% Consider the issue price of Bond at $ 90, and redemption value be $ 105 Calculate the posttax Yield to Maturity for the investor where the rate of normal Income tax can be assumed at 30% and
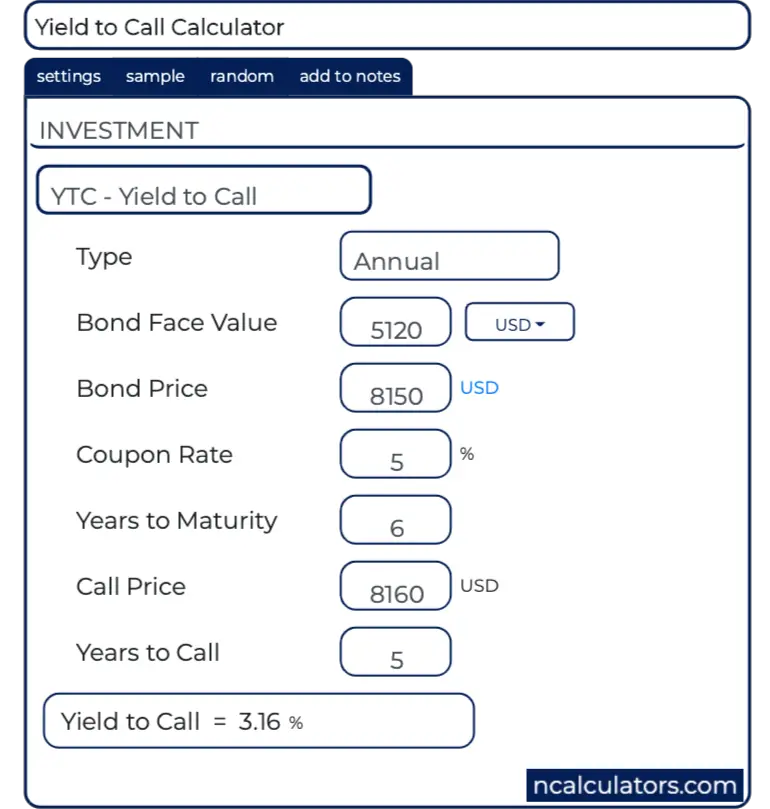


Yield To Call Ytc Calculator



Zero Coupon Bonds Invest In Zero Coupon Bonds Today
N – The number of coupon payments received in each year Practical Example Assume that you purchase a bond with a nominal coupon rate of 7%We can use the above formula to calculate approximate yield to maturity Coupons on the bond will be $1,000 * 8%, which is $80 Yield to Maturity (Approx) = (80 (1000 – 94) / 12 ) / ( (1000 940) / 2) Yield to Maturity will be –Consider a $1,000 zerocoupon bond that has two years until maturityThe bond is currently valued at $925, the price at which it could be purchased today The formula would look as follows (1000



What Is A Zero Coupon Bond



Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Calculations In Debt Mutual Fund Nippon India Mutual Fund
An investor purchased a 5year 4% coupon bond with annual payments at a price of % What is the yield to maturity of this bond?R = discount rate (the yield to maturity)RATE (nper, pmt, pv, fv, type, guess) Here, Nper = Total number of periods of the bond maturity Years to maturity of the bond is 5 years But coupons per year is 2 So, nper is 5 x 2 = 10 Pmt = The payment made in every period It cannot change over the life of the bond The coupon rate is 6% But as payment is done twice a year, the



Bonds Yield To Worst Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



How To Calculate Bond Prices And Yields On The Series 7 Exam Dummies
RATE (nper, pmt, pv, fv, type, guess) Here, Nper = Total number of periods of the bond maturity Years to maturity of the bond is 5 years But coupons per year is 2 So, nper is 5 x 2 = 10 Pmt = The payment made in every period It cannot change over the life of the bond The coupon rate is 6% But as payment is done twice a year, theCoupon vs Yield to Maturity A bond has a variety of features when it's first issued, including the size of the issue, the maturity date, and the initial couponFor example, the US Treasury might issue a 30year bond in 19 that's due in 49 with a coupon of 2%(Do not round intermediate calculations
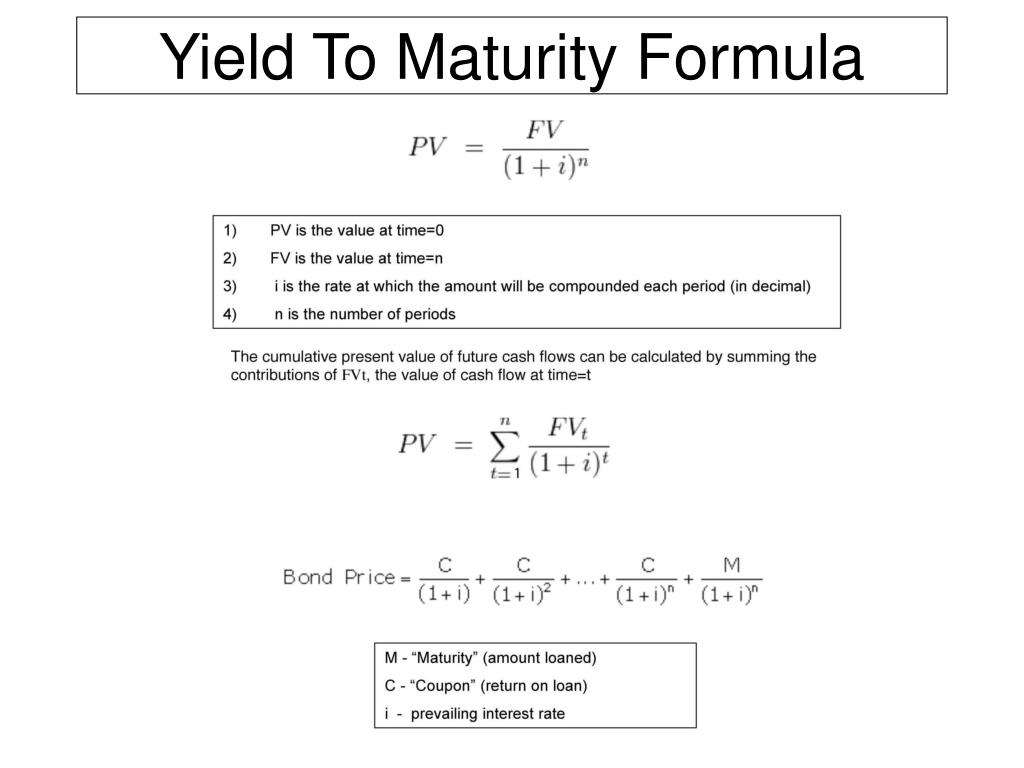


Ppt Yield To Maturity Formula Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Bonds Bond Prices Interest Rates And Holding Period Return Ppt Download
Formula for Calculating the Effective Yield The formula for calculating the effective yield on a bond purchased Effective Yield = 1 (i/n) n – 1 Where i – The nominal interest rate on the bond;If a bond's purchase price is equal to its par value, then the coupon rate, current yield, and yield to maturity are the same Current yield compares the coupon rate to the current market price of the bond For example, if a bond with a face value of $1,000 offers a coupon rate of 5%, then the bond will pay $50 to the bondholder until itsYield to maturity (YTM) is the annual return that a bond is expected to generate if it is held till its maturity given its coupon rate, payment frequency and current market price Yield to maturity is essentially the internal rate of return of a bond ie the discount rate at which the present value of a bond's coupon payments and maturity value is equal to its current market price
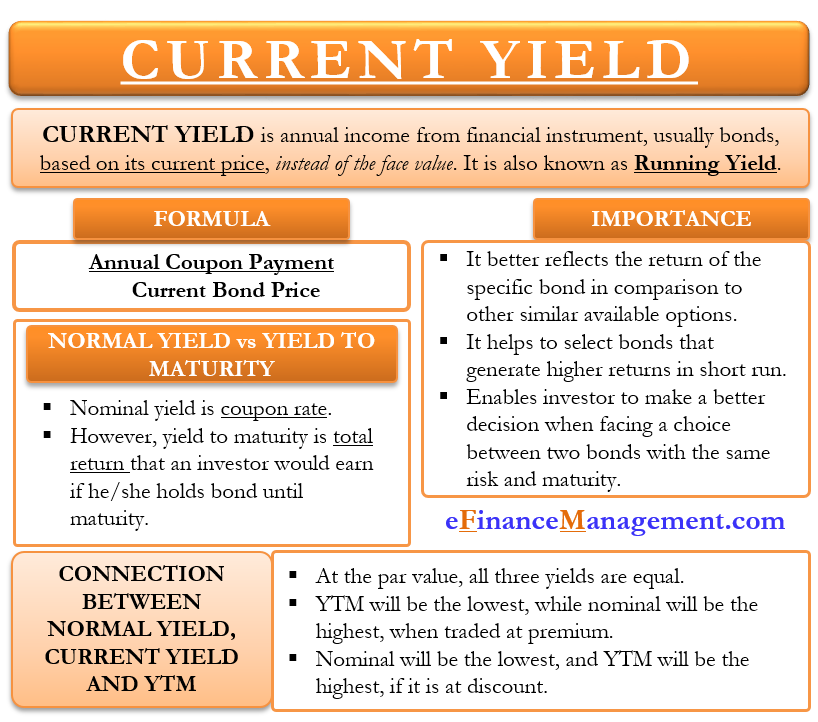


Current Yield Meaning Importance Formula And More
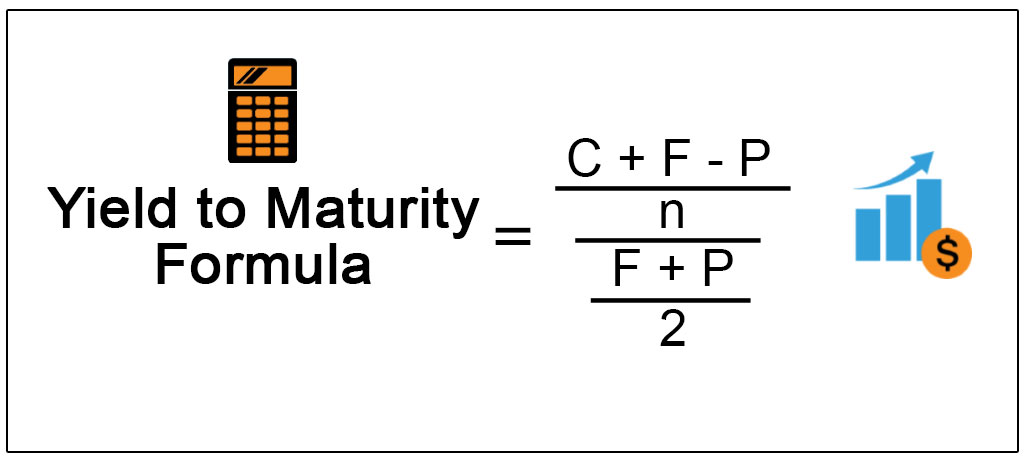


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853%Example of Yield to Maturity Formula The price of a bond is $9 with a face value of $1000 which is the face value of many bonds Assume that the annual coupons are $100, which is a 10% coupon rate, and that there are 10 years remaining until maturity This example using the approximate formula would beCR is the coupon rate Example 1 What is the current yield of a bond with the following characteristics an annual coupon rate of 7%, five years until maturity, and a price of $800?


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Method Example Approximation Excel



Problem Set 1 Tutorial Question Studocu
The coupon rate remains fixed over the lifetime of the bond, while the yieldtomaturity is bound to change When calculating the yieldtomaturity, you take into account the coupon rate and any increase or decrease in the price of the bond For example, if the face value of a bond is $1,000 and its coupon rate is 2%, the interest income equalsYield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (4 days ago) The coupon rate for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853%Solution The yearly coupon payment is $1000 × 7% = $70, using the formula above, we get CY = 70 / 800 * 100 CY = 875%, The Current Yield is 875%



Bond Yield Calculator



Calculating And Using Implied Spot Zero Coupon Rates Bond Math
The first step is to calculate the coupon payment of the bond The coupon is the rate of interest paid to the bondholder This is calculated as the face value multiplied by the coupon rateYou find a bond with 27 years until maturity that has a coupon rate of 90 percent and a yield to maturity of 81 percent Suppose the yield to maturity on the bond increases by 25 percent a What is the new price of the bond using duration and using the bond pricing formula?The approximate yield to maturity of this bond is 1125%, which is above the annual coupon rate of 10% by 125% You can then use this value as the rate (r) in the following formula Bond\ Value = C \bigg( \dfrac{1 (1 r)^{n} }{r} \bigg) \dfrac{F}{(1r)^{n}} C = future cash flows/coupon payments;



Quant Bonds Between Coupon Dates



Finding Ytm Of A Zero Coupon Bond 6 2 1 Youtube
However, in case of couponpaying bonds, yield to maturity is the (somewhat) weighted average of the individual spot interest rates that apply to each cash flow of the bond Let's say we have a 3 year bond with face value of $100 and annual coupon of $0
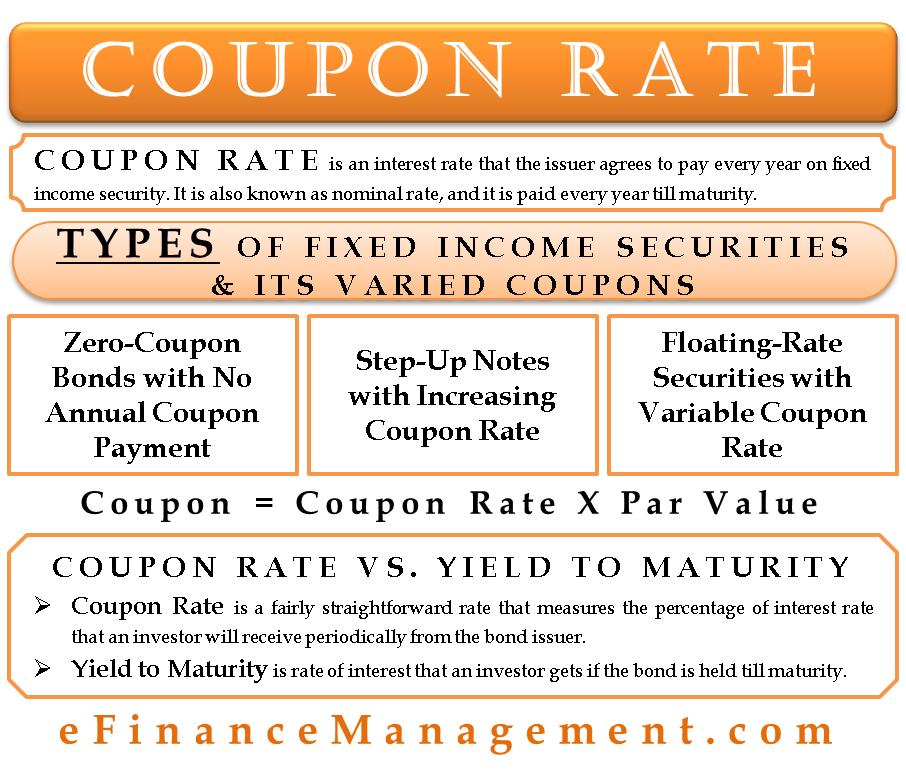


Coupon Rate Meaning Example Types Yield To Maturity Comparision



21 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation



Corporate Finance Berk Demarzo
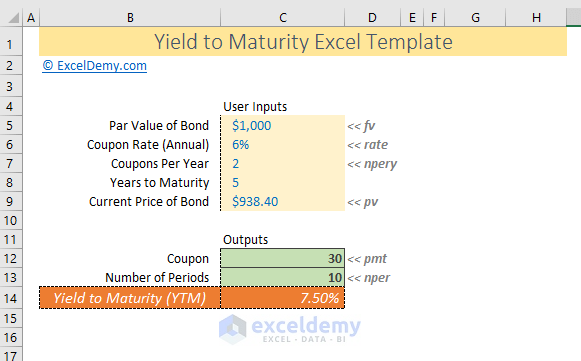


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy



Yield To Maturity Fixed Income


Www Jstor Org Stable


Q Tbn And9gcsk2iegdz1jvuavgo487nzmoaxjpygzrxk8ljgamhuz Bsed74b Usqp Cau
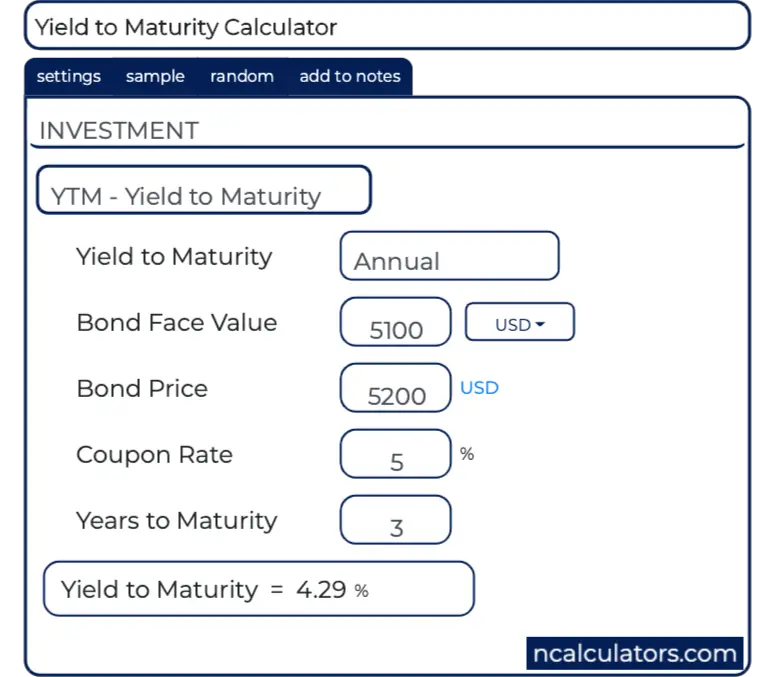


Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity
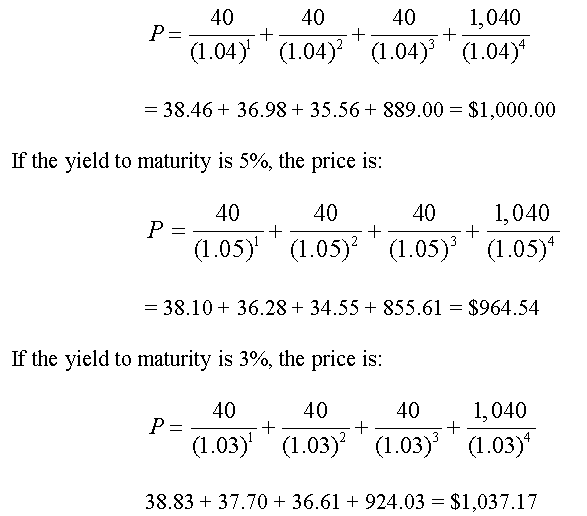


An Introduction To Bonds Bond Valuation Bond Pricing



Workshop 8 Answers Finance 261 Fin261 Studocu


Bond Yield To Maturity



Chapter 6 Bonds 6 1 Chapter Outline 6 1 Bond Terminology 6 2 Zero Coupon Bonds 6 3 Coupon Bonds 6 4 Why Bond Prices Change 6 5 Corporate Bonds Ppt Download


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com
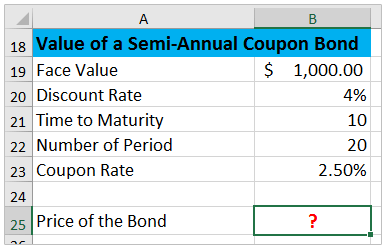


How To Calculate Bond Price In Excel
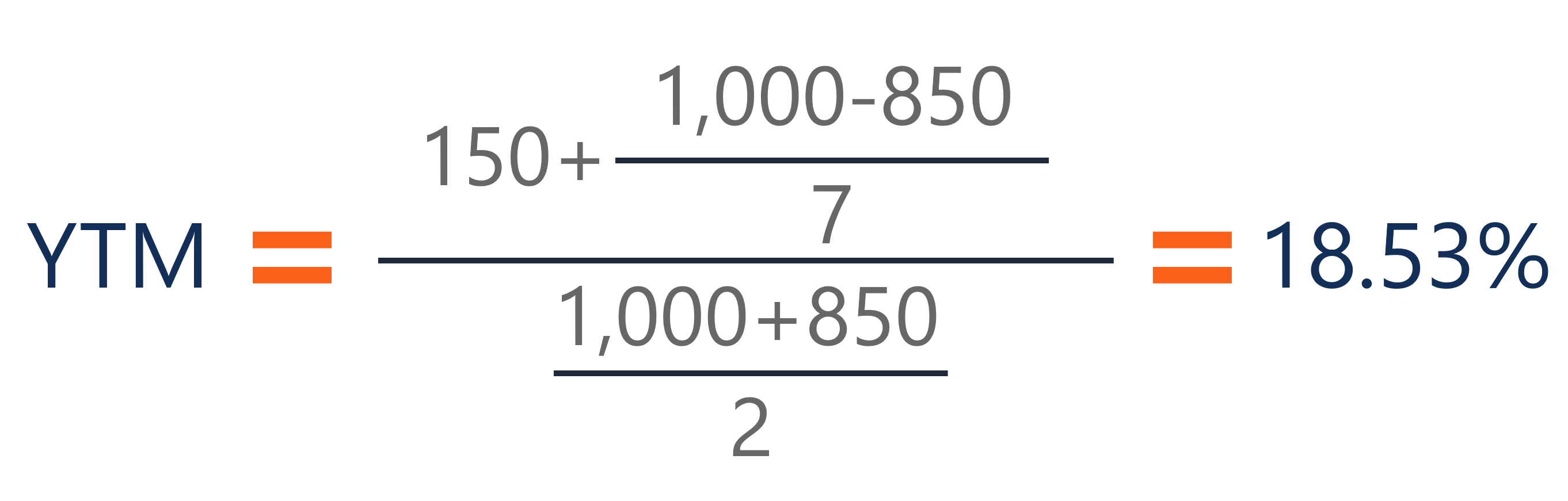


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance


Http Kevinx Chiu Weebly Com Uploads 8 9 8 3 380 Homework 3 Solutions Pdf



Bond Valuation



Coupon Rate Vs Yield Rate For Bonds Wall Street Oasis



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com



Calculate The Coupon Rate Of A Bond Youtube
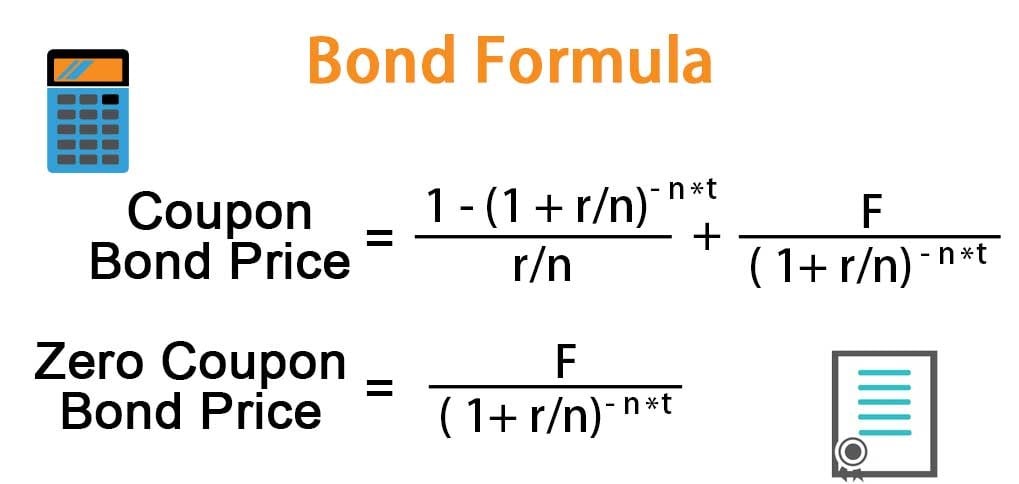


Bond Formula How To Calculate A Bond Examples With Excel Template
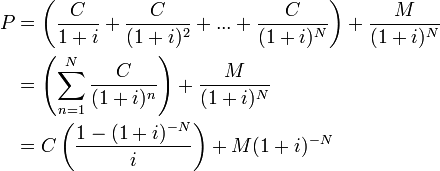


Valuing Bonds Boundless Finance



Solutions To Chapter 6 Valuing Bonds 1 A Coupon Rate 6 Which
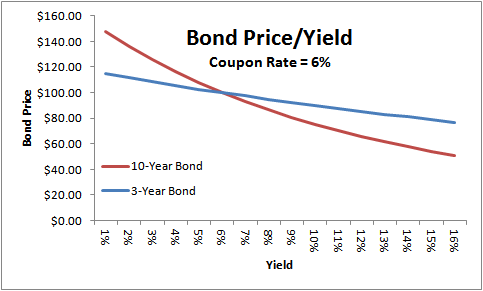


Bond Yields Nominal And Current Yield Yield To Maturity Ytm With Formulas And Examples



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com
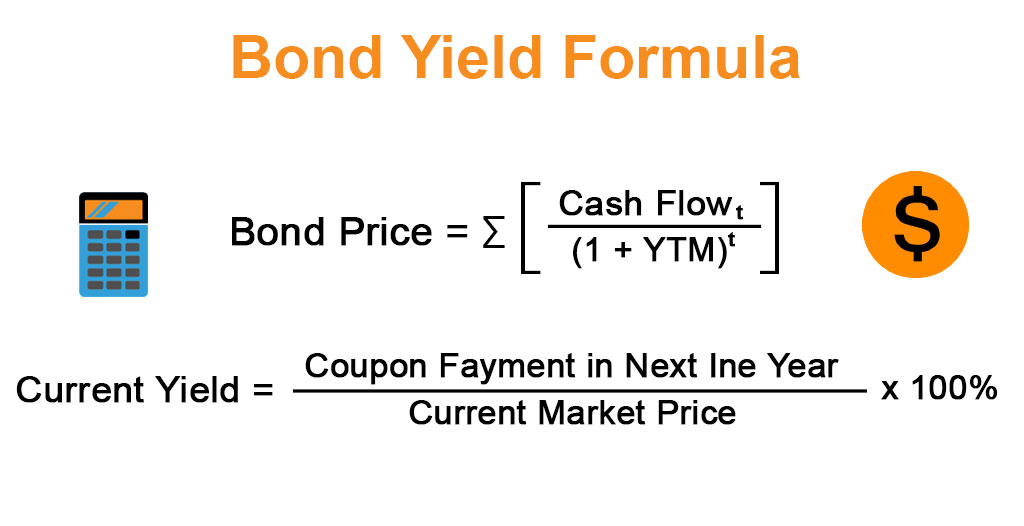


Bond Yield Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template
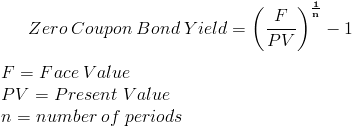


Zero Coupon Bond Yield Formula With Calculator
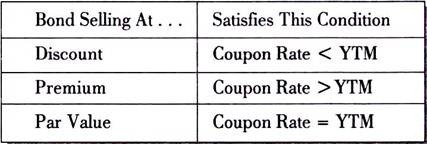


Calculating The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Bond Financial Management



How To Use The Excel Yield Function Exceljet
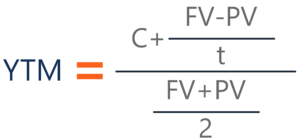


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance
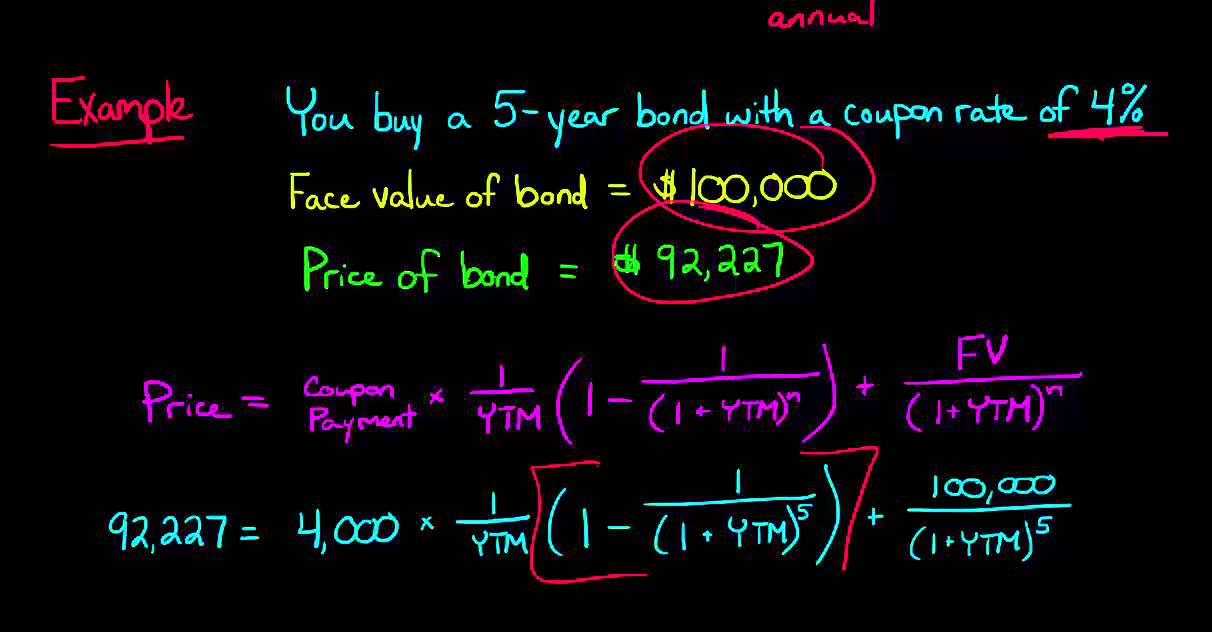


Calculating The Yield Of A Coupon Bond Using Excel Youtube


Http Burcuesmer Com Wp Content Uploads 15 10 Bond Valuation Pdf
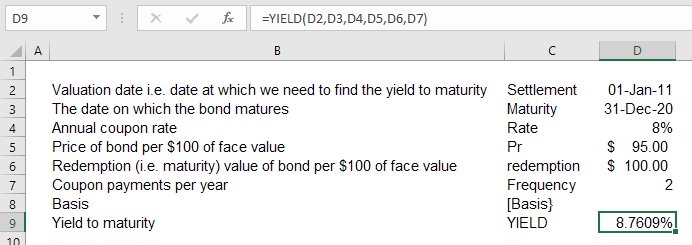


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula And Example



Bond Valuation Wikipedia


Solved Chapter 7 Problem Set Students Must Show Work To Receive Full Credit Compute The Price Of A 9 Coupon Bond With Years To Maturity And A Course Hero



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures



Bonds Yields And Yield To Maturity Economics Online
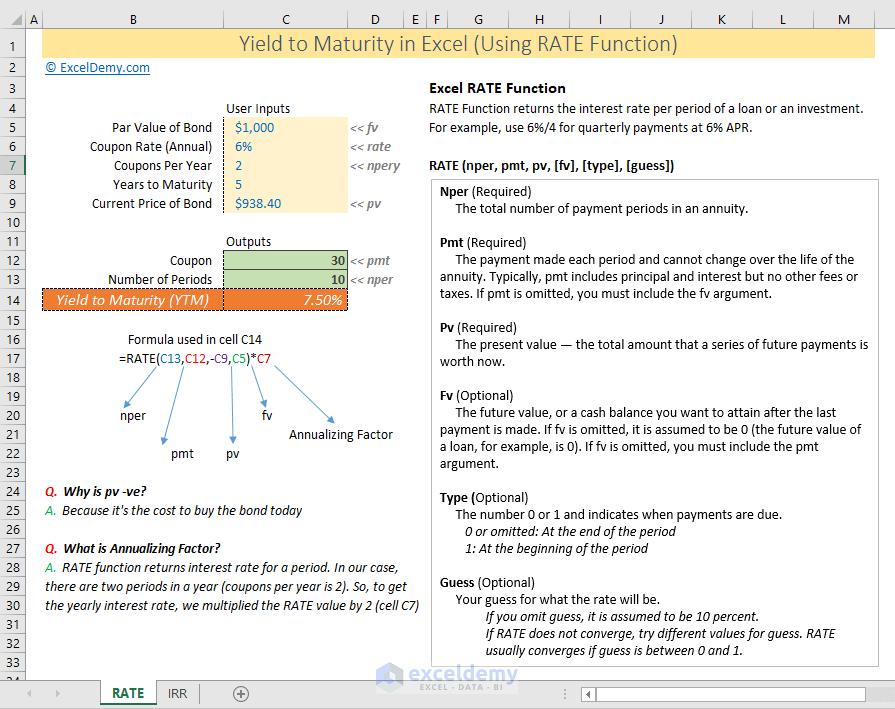


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com
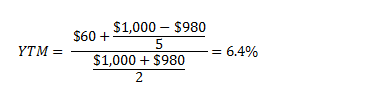


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool


Weighted Average Cost Of Capital Guide Wacc Calculator Excel Download
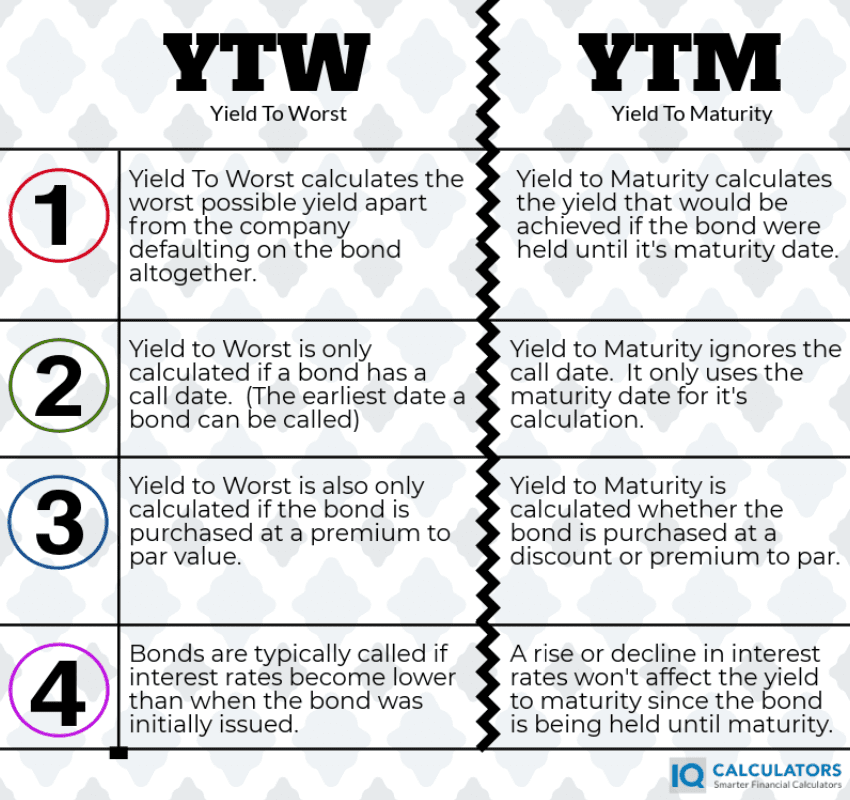


Yield To Worst What It Is And Why It S Important
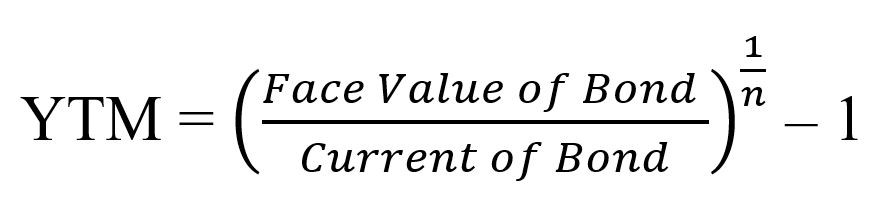


What You Must Know On Bond Valuation And Yield To Maturity Acca Afm Got It Pass


Q Tbn And9gctmjjcknhq5z6xqz1cb0 Ujolevox3tjfw K1tbrzk W Ikim Usqp Cau
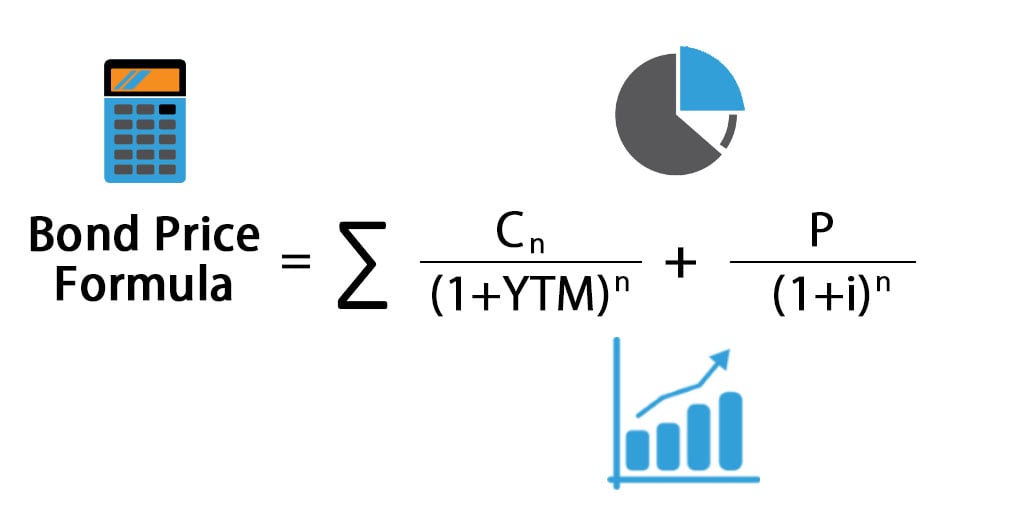


Bond Pricing Formula How To Calculate Bond Price



Yield To Maturity Ytm And Yield To Call Ytc alectures Com


1
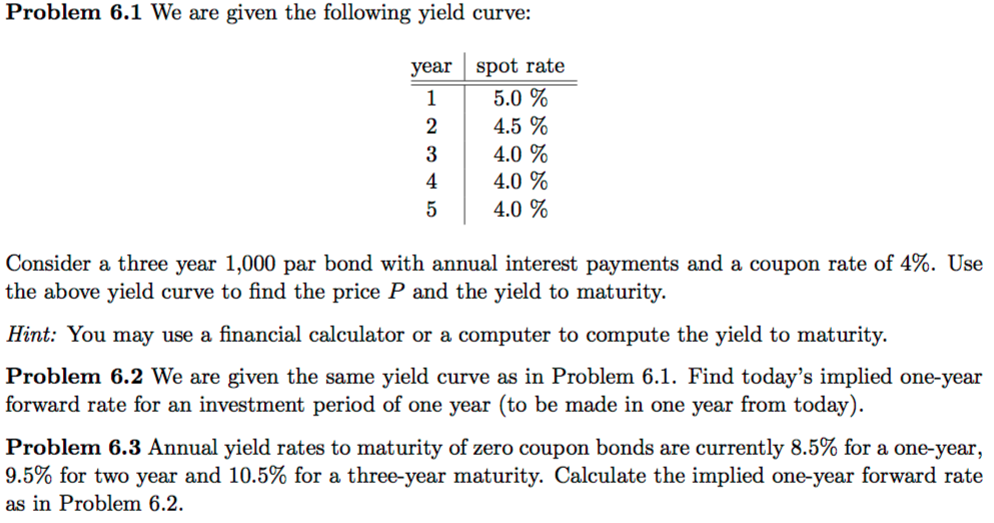


Solved Problem 6 1 We Are Given The Following Yield Curve Chegg Com



Calculate The Ytm Of A Coupon Bond Youtube


What Is The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Zero Coupon Bond With A Face Value Of 1 000 Current Price Of 0 And Maturity Of 4 0 Years Recall That The Compounding Interval


Coupon Bond Formula How To Calculate The Price Of Coupon Bond
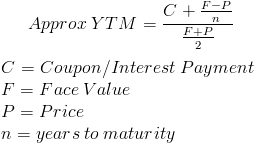


Yield To Maturity Approximate Formula With Calculator



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds
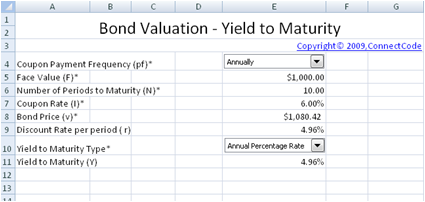


Free Bond Valuation Yield To Maturity Spreadsheet
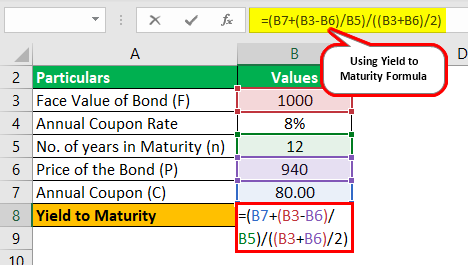


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples


Cost Of Debt Definition Formula Calculation Example
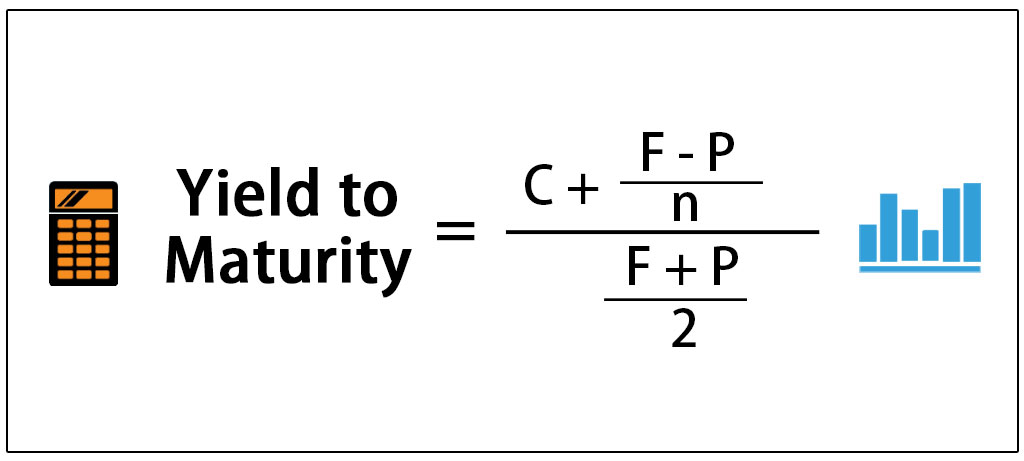


Yield To Maturity Definition How To Calculate Ytm Pros Cons



Yields To Maturity On Zero Coupon Ronds Bond Math
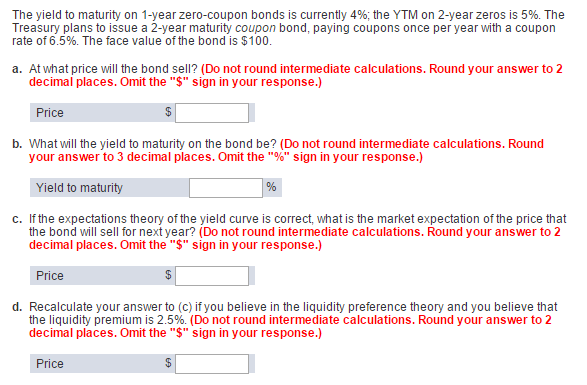


Solved The Yield To Maturity On 1 Year Zero Coupon Bonds Chegg Com
/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)


Yield To Worst Ytw Definition



Calculating The Yield To Maturity Mastering Python For Finance Second Edition


Calculating Yield To Maturity Using The Bond Price



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds



Bond Pricing And Accrued Interest Illustrated With Examples


Learn To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Ms Excel



Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond



Solved Write Down The Formula That Is Used To Calculate T Chegg Com
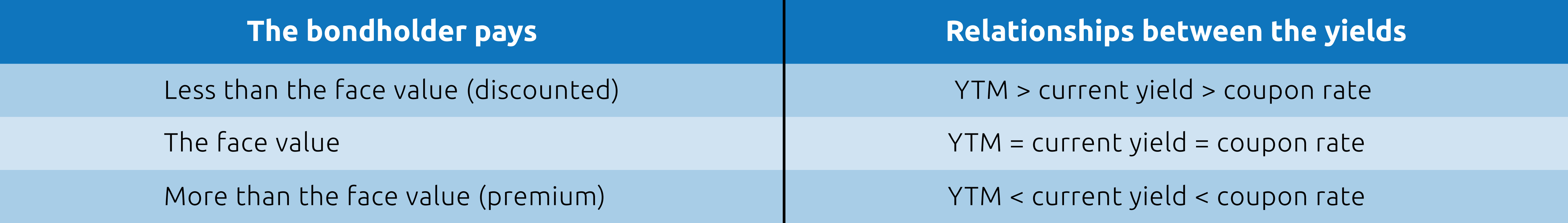


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Calculations In Debt Mutual Fund Nippon India Mutual Fund



What Is Coupon Rate In Bonds Know More Fincash Com


Learn To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Ms Excel


Bond Yield To Maturity Calculator For Comparing Bonds


コメント
コメントを投稿